-
The difference of SFP 10G SR LR LRM ER and ZR
The difference of SFP 10G SR LR LRM ER and ZR SR, LR, LRM, ER and ZR are relatively common types in the 10G IEEE standard, but what's the difference between10g sfp SR, LR, LRM, ER and ZR? To figure out, we need to know the meaning of them first.In fiber optic communications, SR LR LRM ER and ZR are terms that stand for... -
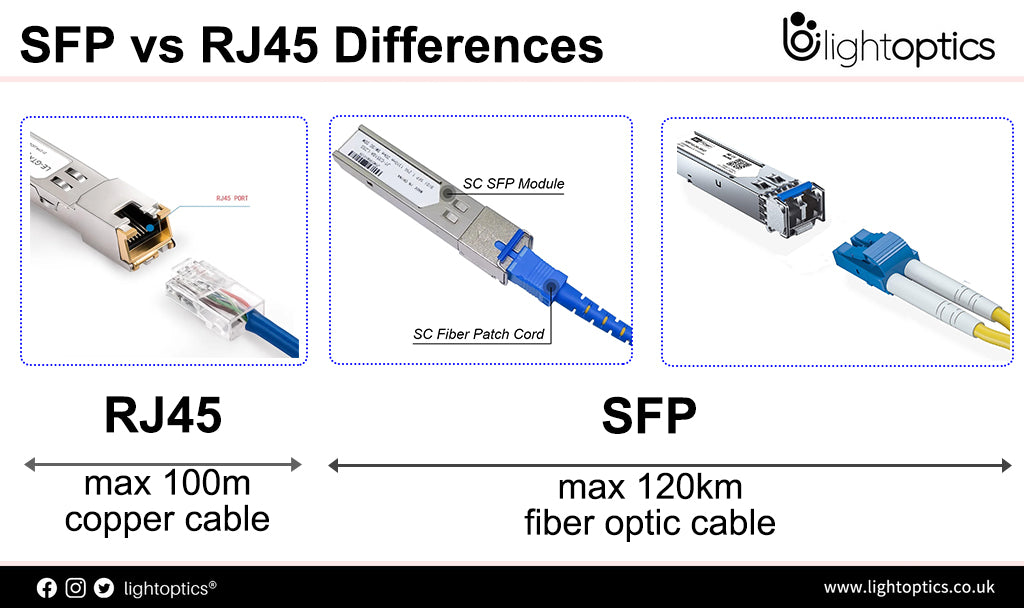
What is the SFP Module? 2024 Best SFP Transceiver Guide
If you're familiar with Ethernet switches, you've likely come across the SFP module. These modules are ubiquitous in modern fiber optic networks, playing a crucial role in connectivity. But what exactly are they?This post serves as a comprehensive guide to the SFP module, covering its definition, working principle, various types, and applications.Let's delve into it. What is an SFP module? Before discussing the SFP... -
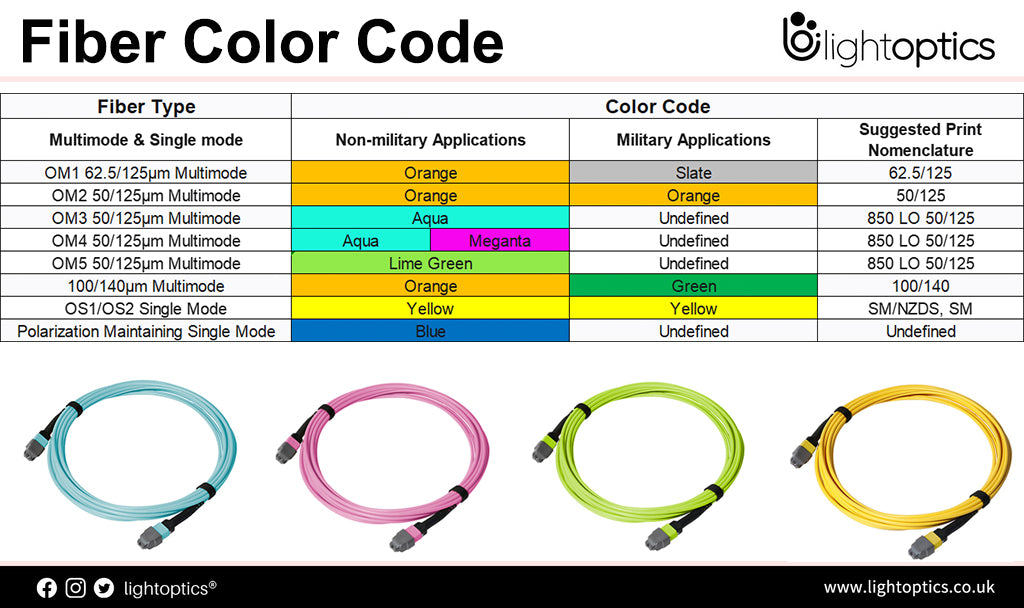
Fiber Color Code
Looking at a large amount of fiber optic cables without any guidance can be confusing. The fiber optic cable color code helps to know how to approach these cables identifying them in an easy way.If you want to understand more about this color system, this article will help you on that mission. What is Fiber Color Code? Fiber color code is a standard for... -
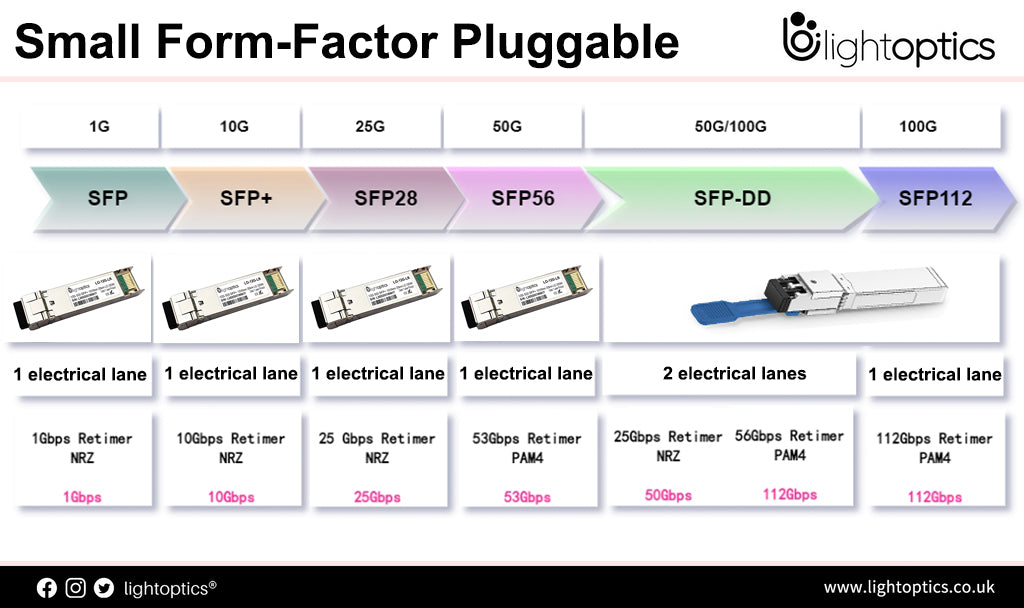
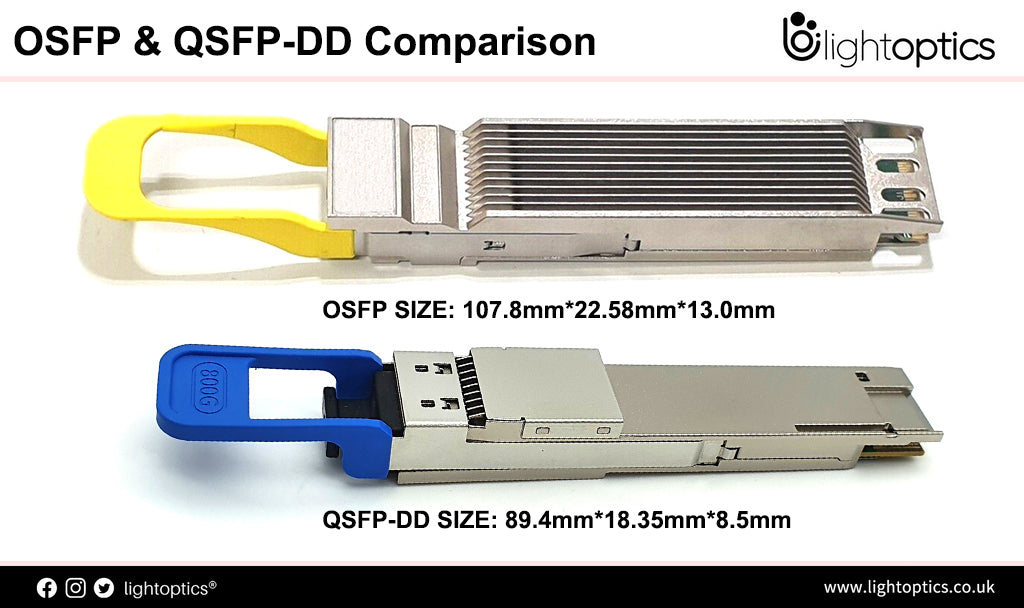
A Guide to 100G Transceiver QSFP28, SFP56-DD, DSFP, SFP-DD, SFP-DD112 Name and Specs
Confused by the name of 100G transceiver optics and cables?The names I usually use for communication are vendor-specific dialects. It's a common story that different interpretations are commonplace next door.The development trend of optical modules is higher speed, smaller packages and lower power consumption. As 100G, 200G, 400G and even 800G high-speed optical transceivers are wided used in data center interconnects and other fiber... -
800G Optical Transceiver Demand Surges with Advancements in AI Computing
In the ever-evolving landscape of information technology, the demand for high-speed and high-capacity data transmission has become more critical than ever. Artificial Intelligence (AI) computing, with its complex algorithms and data-intensive processes, has emerged as a key driver in this paradigm shift. This article explores the surge in demand for 800G optical transceivers, propelled by the rapid growth of AI computing applications. AI Computing... -
200G QSFP56 AOC Introduction and Application
What is a 200G QSFP56 AOC? 200G QSFP56 AOC is a QSFP56 VCSEL (Vertical Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser) based active optical cable (AOC) designed for use in 200Gb/s Ethernet or InfiniBand HDR systems. The 200G QSFP56 AOC offers high-end port density and configurability, and a much longer reach than passive copper cables in the data centers. 200G QSFP56 AOC has a standard SFF-8665 compliant QSFP56... -
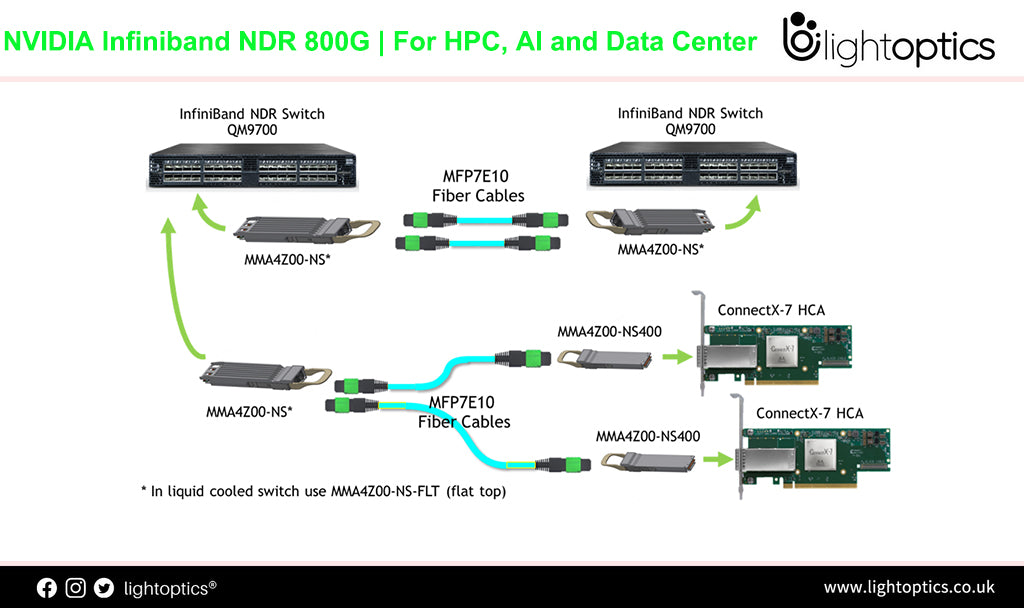
NVIDIA's New Ethernet Networking Platform for HPC, AI and Data Center
NVIDIA's New Ethernet Networking Platform for HPC, AI and Data Center InfiniBand switch Name PN Description 400G InfiniBand switch, managed MQM9700-NS2F 64-ports 400Gb/s, 32 OSFP ports, managed, power-to-connector(P2C) airflow (forward) 400G InfiniBand switch, managed MQM9700-NS2R 64-ports 400Gb/s, 32 OSFP ports, managed, connector-to-power(C2P) airflow (reverse) 400G InfiniBand switch, unmanaged MQM9790-NS2F 64-ports 400Gb/s, 32 OSFP ports, unmanaged, P2C airflow (forward) 400G InfiniBand switch, unmanaged MQM9790-NS2R 64-ports 400Gb/s, 32 OSFP ports, unmanaged,... -
Migrating from GPON to XGS-PON and NG-PON2
Broadband technology and broadband markets are constantly evolving. Service providers need an optical distribution network (ODN) which not only supports today’s requirements for data, video and voice with QoS, SLA agreements and security, but also tomorrow’s requirements. Today bandwidth scalability from GPON (2.5 Gigabit downstream/1.25 Gigabit upstream) to XGS-PON (10 Gbps upstream and downstream) and even NGPON2 (40 Gbps upstream and downstream) services are... -
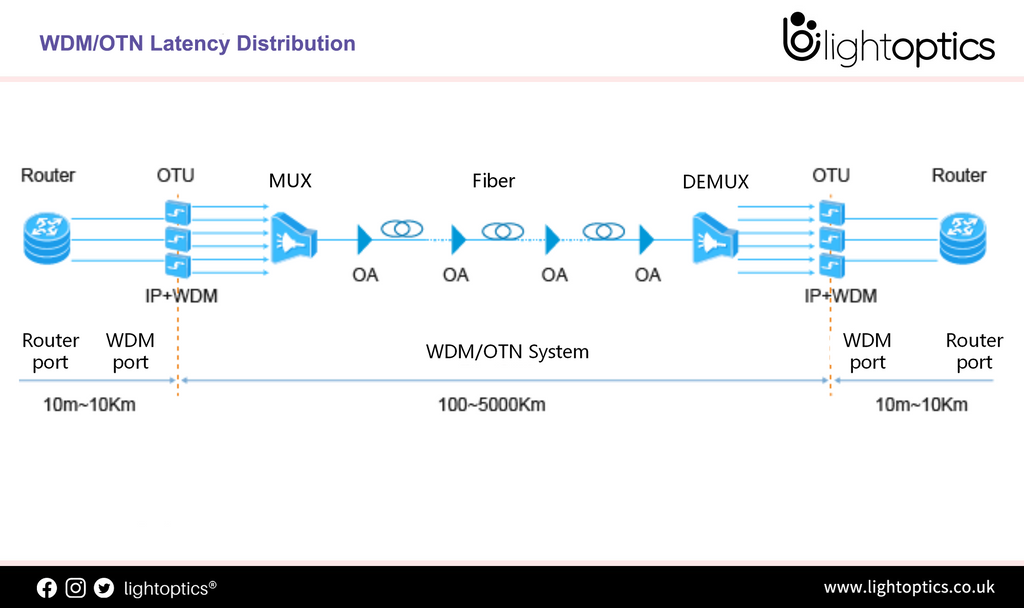
Introduce for WDM/OTN Latency
Introduce for WDM/OTN Latency What does WDM mean? WDM stands for wavelength division multiplexing, a technique used to send multiple channels of data over the same cable in fiber-optic transmission. Fiber-optic cables transmit data via pulses of light, which contain a range of wavelengths or colors. WDM enables each pulse to carry data from different sources on multiple wavelengths. With WDM, a single fiber... -
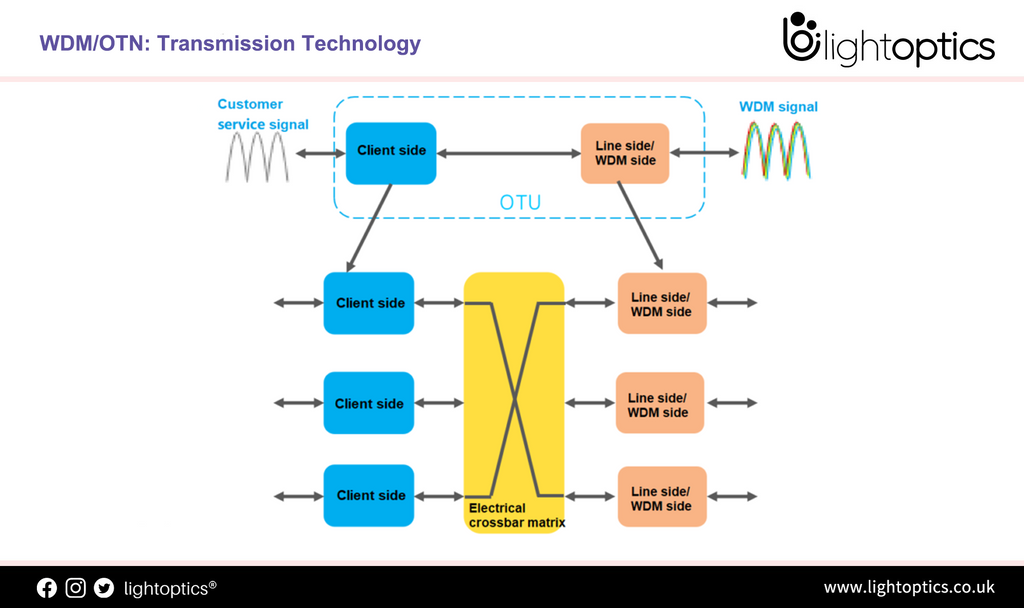
WDM/OTN: Transmission Technology
WDM/OTN: Transmission Technology Modern optical technologies reach the Terabit range and revolutionize the network world. The course takes an inventory and shows development trends. It discusses the major changes in the fields of optical fiber types, access, and backbone, as well as optical networks and network protection and gives a compact overview of the innovative potential of high-performance, optical technologies. WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing)...
Customer Service: sales@lightoptics.co.uk
Shopping Cart
0
Close
Your Cart
Your cart is currently empty.